

This stage is called Saturation Region and the typical voltage allowed across the Collector-Emitter (VCE) or Base-Emitter (VBE) could be 200 and 900 mV respectively. When this transistor is fully biased, it can allow a maximum of 500mA to flow across the collector and emitter. To bias a transistor we have to supply current to base pin, this current (IB) should be limited to 5mA. The maximum amount of current that could flow through the collector pin is 500mA, hence we cannot connect loads that consume more than 500mA using this transistor. The BC548 has a gain value of 110 to 800 which determines the amplification capacity of the transistor.
Researchers are also studying transistors made from special forms of carbon. Germanium, another group-14 element, is used together with silicon in specialized transistors. Transistors are made of semiconductor chemical elements, usually silicon, which belongs to the modern Group 14 (formerly Group IV) in the periodic table of elements. In a MOSFET used as an amplifier, transistors take the flow of the drain and source, and since the source current is so much larger than the drain's current, it is common for the drain's current to rise to the value of the sources, amplifying it. This rivals the mechanical switch, which requires a constant force pressing on it. When the gate of a P-channel MOSFET is positively charged, electricity will flow through, this is useful for electronics that require a switch to be turned on, making it an electronic switch. This means that you can control the same amount of current with a very small amount of current going into the base. One of the transistors is connected so that it controls the current to the base of the other transistor. The basic Darlington transistor circuit is formed from two bipolar transistors wired emitter to base so they act as one transistor. The "B" stands for base, the "C" stands for collector, and the "E" stands for emitter. The circuit symbol of a Darlington transistor. The water is the electrons, and when you positively charge the gate, it unbends the hose, letting water flow. The transistor can also work when the gate is just positively charged, so it doesn't need to be touching the drain.Īn easy way to think of how a transistor works is as a hose with a sharp bend that stops the water from going through. This is because when the gate is positively charged, the positive electrons will push other positive electrons in the transistor letting the negative electrons flow through.
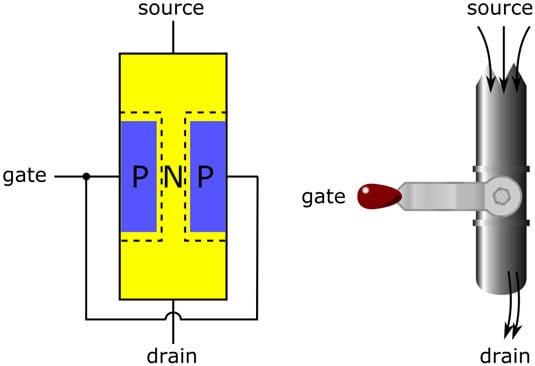
But when power flows through the gate (or base), the transistor will allow electricity through.
#Transistor definition series#
When the source (or emitter) is connected to the negative terminal of the battery, and the drain (or collector) to the positive terminal, no electricity will flow in the circuit (if you have only a lamp in series with the transistor). Transistors have three terminals: the gate, the drain, and the source (on a bipolar transistor, the wires can be called the emitter, the collector, and the base). When the center pin is powered, the power can flow.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
